Policies
Caching
Respond to matched incoming requests with cached content
Configuration#
{
"name": "my-caching-inbound-policy",
"policyType": "caching-inbound",
"handler": {
"export": "CachingInboundPolicy",
"module": "$import(@zuplo/runtime)",
"options": {
"expirationSecondsTtl": 60,
"dangerouslyIgnoreAuthorizationHeader": false,
"headers": [
"header_used_as_part_of_cache_key"
],
"cacheHttpMethods": [
"GET"
]
}
}
}Options#
namethe name of your policy instance. This is used as a reference in your routes.policyTypethe identifier of the policy. This is used by the Zuplo UI. Value should becaching-inbound.handler/exportThe name of the exported type. Value should beCachingInboundPolicy.handler/modulethe module containing the policy. Value should be$import(@zuplo/runtime).handler/optionsThe options for this policy:cacheIdOptional, specifies an id or 'key' for this policy to store cache. This is useful for cache-busting. For example, set this property to an env var and if you change that env var value, you invalidate the cache.
dangerouslyIgnoreAuthorizationHeaderBy default, the Authorization header is always considered in the caching policy. You can disable by setting this to true
headersThe headers to be considered when caching
cacheHttpMethodsHTTP Methods to be cached - defaults to GET if none specified. Valid methods are: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, HEAD
expirationSecondsTtlThe timeout of the cache in seconds
statusCodesResponse status codes to be cached - defaults to 200, 206, 301, 302, 303, 404, 410 if none specified
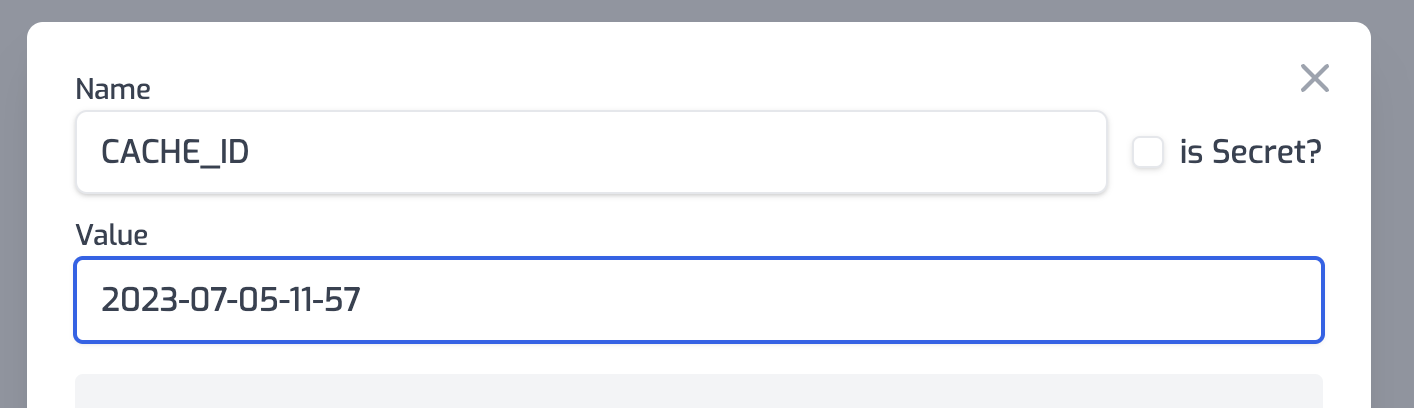
Cache-busting
If you need to support cache-busting on demand, we recommend applying a
cacheId property based on an Environment Variable. Ensure all your cache
policies are using a cachedId based on a variable and then change that variable
(and trigger a redeploy) to clear the cache.
e.g.
{
"export": "CachingInboundPolicy",
"module": "$import(@zuplo/runtime)",
"options": {
"cachedId": "$env(CACHE_ID)", // this is reading an env var
"expirationSecondsTtl": 60,
"dangerouslyIgnoreAuthorizationHeader": false,
"headers": ["header_used_as_part_of_cache_key"]
}
}Then you would setup an env var for this, we recommend using the current date it
was set, e.g. 2023-07-05-11-57 and then simply change this value and trigger a
redeploy to bust your cache.